An Overview
Unlike the yesteryears, data is flowing to and from many directions via the cloud, legacy systems, ERPs, on-premise applications, etc. Data integration is a process that combines data from several disparate sources, which are stored using various technologies and provide an incorporated form and structure. Data integration becomes increasingly important in cases of mergers, acquisitions, and/or consolidation of applications to provide a unified view of company’s data assets. Bringing data from these disparate source systems into a common decision-making framework exponentially proliferates data worth.
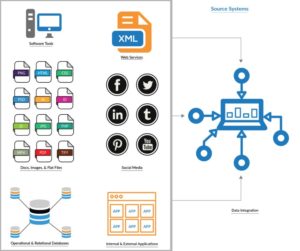
Data integration aligns, combines, and presents data sets from internal and external sources to support the analytical processing of enterprise data, thus fulfilling the data integration objective.
The Challenges
Superfluity of technological modernization varying from automation to interconnectivity of almost everything is leading to an overpowering amount of data. Enterprises that effectively utilize data to analyze trends and gather new insights are leading the respective industries. The following are the typical data challenges that drive enterprises to strategize Data Integration initiatives:

Data integration is very crucial to every business process, and hence the need to integrate all enterprise data. Here are the reasons why organizations should have data integration on a top priority:
- Varied Data Sources
Data is growing exponentially and is expected to be at 44 trillion gigabytes by 2020, connecting about 30 billion digital devices, 40% of it touched by the cloud, as researched by EMC Digital Universe.
- Data Analytics
Effective decision-making is a reality when data integration happens in real-time or near real-time and spans across the data landscape. Faster analytics is possible only if data is available in a single platform.
- Lead Generation
Enterprises need to generate more business to reach the revenue targets. It becomes inevitable for marketers to amalgamate customer data sources and enterprise data sources to make best possible business decisions, paving the way to customer delight.
A smart data integration strategy provides a way to close deals faster, increase revenue, and improve customer loyalty. The journey from data integration to actionable insights requires organizations to overcome challenges around Data Integration.
The Benefits
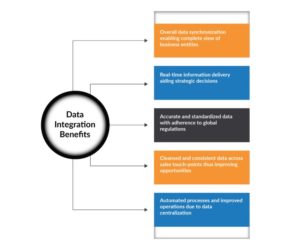
The benefits of integration are not limited to information sharing, but extended to sophisticated adjustments in process and practice within source systems resulting in an overall improvement. Modern data integration hubs are designed to support personnel and processes that include data, architects, analysts, and stewards while aligning with business users. Here are the benefits of data integration:
Enterprise Data Integration Solutions
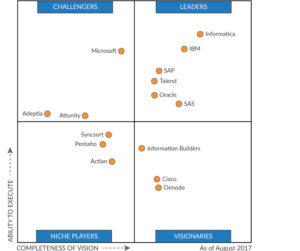
A leading industry analyst’s quadrant for data integration tools named Informatica and IBM as market leaders.
Informatica’s Data Integration Hub
Informatica’s modern data integration infrastructure combines advanced hybrid data integration capabilities and centralized governance with flexible self-service business access for analytics. Informatica offers enterprise-oriented data integration solutions to cater to every business need.
- Data Integration Hub – Modern publish/subscribe hub architecture for data and cloud integration. Informatica Integration Hub combines automated and efficient hybrid data integration orchestration with self-service capabilities to empower distributed team collaboration.
- PowerCenter – The industry’s only fully-integrated, end-to-end enterprise data integration platform. Informatica PowerCenter forms the foundation for all data integration initiatives, including analytics and data warehousing, application migration, or consolidation and data governance
- B2B Data Exchange – Modern intercompany exchange to securely and collaboratively integrate any data with partner networks to drive growth and profitability
IBM
IBM offers a unified integration platform that transforms structured and unstructured data and delivers it to any system on a scalable big data platform. IBM’s data integration platforms support rapidly-evolving varied business needs by way of flex-point licensing.
- IBM InfoSphere Information Server for Data Integration – Transforms data in any style and delivers it to any system, resulting in faster time-to-value. It is enabled with built-in transformation functions and a common metadata framework that increases efficiencies, and offers multiple options for delivering data – bulk ETL, virtual, and incremental
- IBM BigIntegrate – A big data integration solution providing superior connectivity, fast transformation, and reliable, easy-to-use data delivery features that execute on the data nodes of a Hadoop cluster. It provides a flexible and scalable platform to transform and integrate your Hadoop data.
- IBM DataStage – DataStage is a leading ETL platform that integrates data across multiple enterprise systems by leveraging a high performance parallel framework, available on-premises or on the cloud, and supports extended metadata management and scalable, big data enterprise connectivity. It integrates heterogeneous data, including big data at rest or big data in motion, on both distributed and mainframe platforms.
Conclusion
Modern data integration technologies eliminate traditional tradeoffs and enable data management teams to execute better, cheaper, and faster projects. A data integration approach that focuses on people, processes, and technologies, takes advantage of best practices and tools that have steadily matured with greater capabilities and reach to drive an evolution toward the ideal of an agile, data-driven enterprise.

Michele Davidovich
Client Solutions Executive




















